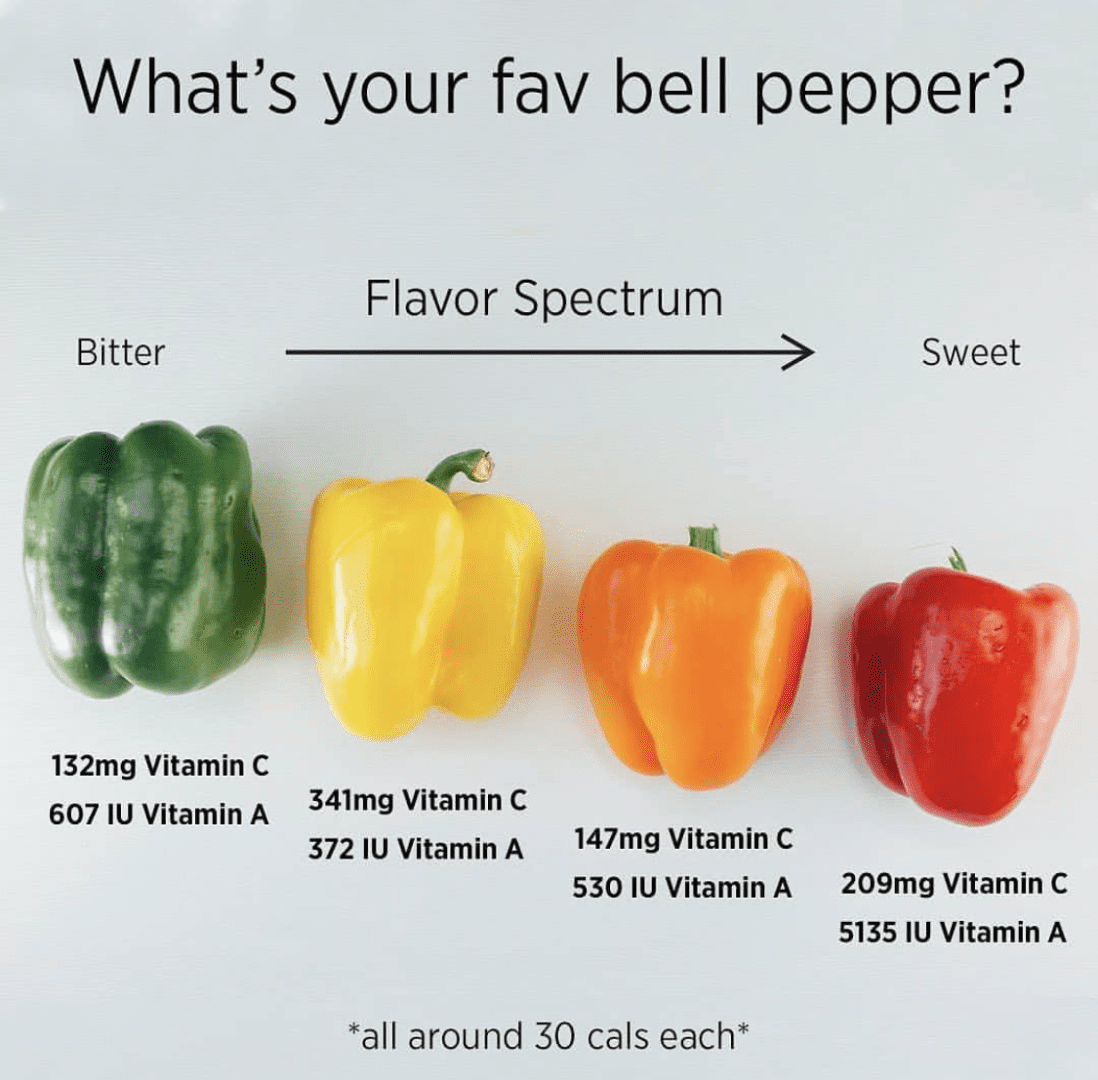
Exploring the Spectrum: A Guide to Bell Pepper Varieties from Green to Red
Bell peppers are not only vibrant and flavorful, but they also come in a variety of colors and tastes, each offering its own unique culinary and nutritional benefits. From the crunchy, green bell pepper to the sweet, red one, understanding the differences between these peppers can elevate your cooking and nutrition game. In this blog post, we’ll explore the varieties of bell peppers, tracing their journey from green to red, and everything in between.
1. Green Bell Peppers: The Unripe Gem
Green bell peppers are the first stage of bell pepper maturation. They are harvested before they fully ripen, which is why they have a slightly bitter and grassy flavor compared to their sweeter counterparts. Despite their more robust taste, green bell peppers are still packed with nutrients:
- Vitamin C: Green bell peppers are an excellent source of Vitamin C, essential for immune function and skin health.
- Vitamin K: This vitamin plays a crucial role in blood clotting and bone health.
- Antioxidants: They contain various antioxidants, including lutein and zeaxanthin, which support eye health.
Green bell peppers are perfect for adding a crunchy texture and fresh flavor to salads, stir-fries, and sandwiches. They also hold up well when cooked, making them a great choice for grilling or roasting.
2. Yellow Bell Peppers: The Sweet Transition
As bell peppers ripen, they transition from green to yellow. Yellow bell peppers are sweeter than their green counterparts and have a more mellow flavor. They offer a slightly tangy taste and are rich in nutrients:
- Vitamin C: Yellow bell peppers have a higher Vitamin C content than green peppers, contributing to immune system health.
- Vitamin A: They are a good source of Vitamin A, important for vision and skin health.
- Carotenoids: Yellow bell peppers contain carotenoids like beta-carotene, which have antioxidant properties and support overall health.
Yellow bell peppers are fantastic for adding a burst of color and sweetness to dishes. They’re ideal for salads, salsas, and as a colorful addition to stir-fries and roasted vegetable medleys.
3. Orange Bell Peppers: The Sweet Spot
Orange bell peppers are another stage of ripeness, bridging the gap between yellow and red. They offer a sweet and slightly tangy flavor, making them a versatile ingredient in a variety of dishes. Nutritionally, orange bell peppers offer:
- Vitamin C: They are rich in Vitamin C, similar to yellow bell peppers.
- Vitamin A: Orange peppers also provide a good amount of Vitamin A.
- Antioxidants: They are high in carotenoids, including beta-carotene and cryptoxanthin, which contribute to their vibrant color and health benefits.
Orange bell peppers are great for adding a sweet, fruity flavor to salads, stir-fries, and roasted vegetable dishes. Their bright color makes them an appealing addition to any meal.
4. Red Bell Peppers: The Sweetest of Them All
Red bell peppers are the final stage of ripeness and are known for their sweet, rich flavor and tender texture. As bell peppers ripen from green to red, their natural sugars develop, making them the sweetest of the bell pepper varieties. Nutritionally, red bell peppers are a powerhouse:
- Vitamin C: Red bell peppers contain even more Vitamin C than their yellow and green counterparts.
- Vitamin A: They are an excellent source of Vitamin A, thanks to their high beta-carotene content.
- Antioxidants: Red bell peppers are rich in antioxidants like lycopene, which has been linked to various health benefits, including reduced risk of certain cancers.
Red bell peppers are perfect for snacking, adding to salads, or roasting to enhance their natural sweetness. They’re also a key ingredient in many Mediterranean and Middle Eastern dishes.
5. Lesser-Known Varieties
In addition to the classic green, yellow, orange, and red bell peppers, there are also other less common varieties worth noting:
- Purple Bell Peppers: These peppers have a rich, deep color and a slightly tangy flavor. They are high in antioxidants and can add a unique touch to any dish.
- Chocolate Bell Peppers: These peppers have a darker brown color and a sweet, earthy flavor. They’re less common but offer a unique taste experience.
Conclusion
Bell peppers are a versatile and nutritious vegetable that come in a rainbow of colors, each with its own unique flavor and nutritional profile. From the grassy bite of green bell peppers to the sweet richness of red peppers, incorporating a variety of bell peppers into your diet can enhance both the taste and nutritional value of your meals. Whether you’re adding a pop of color to a salad or roasting them for a flavorful side dish, bell peppers are sure to brighten up your culinary creations.
Share this post using the icons below.